Green Tea & Brain Health: MRI Insights into Dementia Prevention 🍵
Overall Insight
Japanese scientists have discovered that consuming 600 millilitres of green tea a day can reduce the risk of dementia in the elderly.
The recent study, published in “npj:Science of Food“ 07 January 2025, examined that out of a group of nearly 9000 older adults, those who regularly drank green tea exhibited fewer white matter lesion on their MRI scans, compared to non-drinkers.
This discovery suggests how diet plays a vital role in neurological health.
Understanding White Matter Lesions Through MRI
White matter lesions (WMLs) are small areas of damage in the brain’s white matter, which is associated with cognitive decline & dementia.
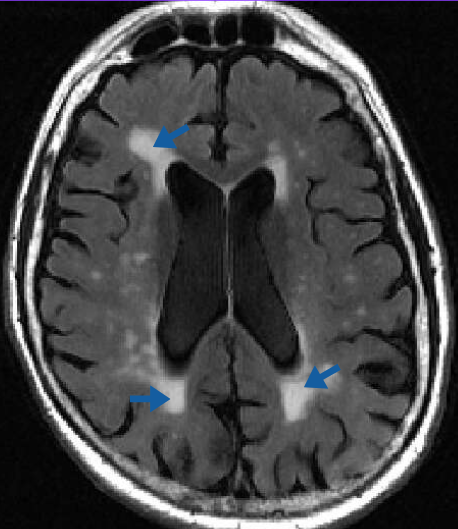
Blue arrows on MRI image of human brain showing multiple white matter lesions
Credit: Elsevier/Academic Radiology
In the study, MRI scans demonstrated that individuals who consumed green tea regularly had significantly fewer white matter lesions than those who did not. The findings suggest that green tea’s bioactive compounds, particularly polyphenols, may offer neuroprotective benefits that help preserve brain structure.
Japanese Study on Green Tea and Dementia Risk
A team of Japanese researchers from multiple universities, including Kanazawa, Kyushu, Hirosaki, and Keio, explored the link between green tea consumption and cognitive health. Conducted between 2016 and 2018, their study involved 11,410 individuals aged 65 and older, with MRI scans performed on 9,646 participants.
All participants were required to fill out a Food Frequency Questionnaire to record their consumption of green tea and coffee. The daily intake of green tea and coffee were classified into four groups: 0–200, 201–400, 401–600, and more than 600 milliliters (ml). After the 24 month period, the participants also underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans to assess their cerebral white matter lesions, hippocampal volume, and total brain volume.
Participants who consumed 600 millilitres (approximately three cups) of green tea per day showed three percent less white matter damage than those who drank 200 millilitres or less.
Furthermore, individuals who consumed 1,500 millilitres of green tea daily exhibited six percent less damage compared to the control group.
Additionally, researchers also found that there was no association between drinking cofee and decreased presense of white matter lesions in the brain. This is most likely due to the composition of coffee, which is mostly from chlorogenic acid and caffeine, whereas green tea is composed of caffeine, catechins, chlorophyll, theanine, vitamins, and minerals.
The Role of Polyphenols in Brain Health
Green tea is rich in polyphenols, powerful antioxidants known for their anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. These compounds have been shown to reduce oxidative stress and improve blood flow to the brain, both of which are critical factors in maintaining cognitive function. By limiting the development of white matter lesions, green tea could contribute to a lower risk of dementia and related neurological disorders.
Implications for Radiographers and MRI Professionals
As imaging technology continues to advance, integrating dietary habits into patient evaluations could provide a more comprehensive understanding of disease progression and prevention.
While green tea consumption alone is not a guaranteed safeguard against dementia, its potential role in reducing brain lesions highlights the need for further research into diet-based interventions for cognitive health. As the intersection of nutrition and neuroimaging gains more attention, radiology professionals are in a unique position to contribute valuable insights into how lifestyle choices influence brain structure and function.
Final Insight
The connection between green tea consumption and reduced white matter lesions presents a compelling case for the role of diet in brain health. MRI technology has been instrumental in uncovering these links, offering new perspectives on dementia prevention. As scientific understanding grows, incorporating dietary considerations into radiological assessments could help pave the way for more personalised and effective approaches to neurological care.
💡For those looking to support their cognitive health, a simple addition to their daily routine—drinking green tea—might just be a step in the right direction. 🍵
To Read the Official Published Paper: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41538-024-00364-w
Another Link to have a read:
